Flux Core Arc Welding (FCAW) is a Welding arc electric wire with their flux (protective central core). FCAW is a combination of process GMAW welding, SMAW, and SAW. This FCAW welding energy source uses a DC or AC electric current drawn from power plants or through a transformer or rectifier.
FCAW welding is one type of electric welding the working process of supplying filler wire welding electrodes or mechanically continuously into the electric arc. Welding wires or electrodes used for welding FCAW are made of thin metal cylindrical rolled then it is filled with flux according to its usefulness.
Table of Contents :
FCAW Welding Definition, Process, and Wire Classification:
FCAW welding process is the same as GMAW welding, but the difference is a welding wire or tubular-shaped electrode containing a flux while GMAW Solid solid-shaped. Based on the protective methods, Welding FCAW may be divided into two.
FCAW Process:
- FCAW SS (Self-shielding).
Which is the process of protecting the weld metal that is melted by using gas from the evaporation or reaction of the core flux. - FCAW G (Gas shielding).
Is protected with dual gas, which protects the weld metal is melting by using its own gas also added a protective gas that comes from outside the system. The above two methods together produce weld slag from the flux in the welding wire that serves to protect the weld metal when the freezing process. However, the difference lies in the method of the above additional gas supply system and a welding torch (welding gun) is used.
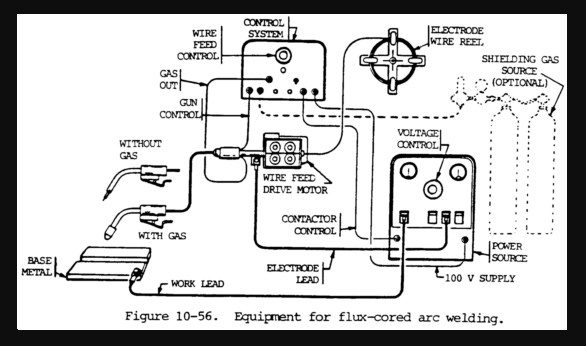
Welding FCAW by way of operation is divided into two:
- Automatic (machine automatic).
- Semi-automatic (semi-automatic).
The main properties (Principal features) block, owned by FCAW in the welding process:
- FCAW welding metallurgy has a nature that can be controlled with the selection of flux.
- FCAW has high productivity because it can supply continuous welding electrodes.
- When the formation of beads or ridges molten weld slag can be protected by a thick FCAW welding generally uses CO2 gas or CO2 mixtures with argon as a protective gas. But to avoid weld metal-contaminated air outside or avoid porosity it must be election-containing flux that has oxygen binding properties or deoxidizer.
FCAW Character Machine And Process:

FCAW welding machines according to the current are divided into three kinds, namely direct current welding machine or Direct Current (DC), alternating current welding machine or Alternating Current (AC), and a welding machine that is double the current welding machine which can be used for welding with direct current (DC) and welding with alternating current (AC). Welding current DC can be used in two ways: straight polarity and reversed polarity.
DC welding machine straight polarity (DC-) is used when the melting point of the parent material of high and large capacity, to holders of electrodes connected to the negative pole and a metal stem, is connected to the positive pole, while the welding machine DC reverse polarity (DC +) is used when the melting point materials lower stem and small capacity, to holders of filler, is connected to the positive pole and the metal stem is connected to the negative pole.
Choice when using DC negative or positive polarity is determined primarily electrode used. Some FCAW fillers are designed to be used only in DC- or DC +. Other fillers can be used in both DC- and DC +.
See: Definition Of Welding and The History
Applications FCAW:
- Carbon steel.
- Steel hard facing and cladding.
- Stainless steel.
- Cast Iron.
- Low alloy carbon steel.
- Sheet steel spot welding
FCAW Welding wire classification:

In the welding of carbon steel and low alloy steel, the flux-cored electrode that is widely used is the type T-1 (acid slag), T-2 (single-pass welding), and T-5 (basic slag).
- Electrode T-1 has good welding properties but does not help keep the acid slag into a low hydrogen weld metal unless specially manufactured. Only a certain amount of flux-cored electrode is eligible for low hydrogen and this is the most widely available of the type T-1.
- Electrode type T-2 is designed for single pass welding on rusted metals and has a deoxidizer Mn and Si higher. Electrodes T-2 are never to be used for multipass welding due to the increase of Mn and Si causing the tensile strength of weld metal that is not dissolved will increase in size, causing problems with cracks when being welded or the use of sour service conditions.
- T-type electrode 5 has a basic slag containing lower hydrogen weld metal and increases the impact properties and resistance to cracking satisfactory. Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of FCAW:
- The FCAW-g process has the advantage of deeper penetration and a higher charging rate than the SMAW process. Thus the welding process is becoming more economical in jobs in welding workshops.
- Filler metal FCAW-SS eliminates the need for external shielding gas and tolerates stronger wind conditions without causing porosity.
Disadvantages of FCAW:
- FCAW-G and FCAW-SS both form a slag layer to be eroded between the layers of the weld.
- The FCAW-g process produces more smoke than GMAW solid wire. Wire FCAW-SS even cause more smoke, so that the work in workshops welding required adequate ventilation, and sometimes require special tools to smoke exhaust in the welding gun.
In the above article about the FCAW Welding process and definition in the article, you can look at FCAW wire classification and more information. For FCAW Welder is the same as GMAW, but if the certificate welder FCAW cannot use to welder GMAW or other processes. Because the standard or code in ASME different process must do requalification.




